Deficient Fluid Volume NANDA Definition: Decreased intravascular, interstitial, and/or intracellular fluid. This refers to dehydration, water loss alone without change in sodium
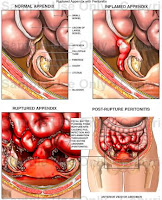
Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the thin tissue that lines the inner wall of the abdomen and covers most of the abdominal organs. Peritonitis may be localised or generalised, and may result from infection (often due to rupture of a hollow organ as may occur in abdominal trauma or appendicitis) or from a non-infectious process.
Nursing Interventions Deficient Fluid Volume - Nursing Care Plan for Peritonitis
Independent:
1. Monitor vital signs, note the presence of hypotension (including postural changes), tachycardia, tachypnea, fever. Measure CVP if any.
Rational: To assist in the evaluation of the degree of fluid deficit / effectiveness of fluid replacement therapy and response to treatment.
2. Maintain adequate intake and output and then connect with the body weight daily.
Rationale: Demonstrates overall hydration status.
3. Rehydration / resuscitation fluid
Rationale: To meet the need of fluid in the body (homeostasis).
4. Measure specific gravity of urine
Rationale: Demonstrates changes in hydration status and renal function.
5. Observation of skin / mucous membranes for dryness, turgor, note peripheral edema / sacral.
Rational: Hypovolemia, fluid displacement, and lack of nutrition aggravate skin turgor, adding tissue edema.
6. Eliminate the danger signs / smells from environment. Limit intake of ice cubes.
Rational: Lowering the gastric stimulation and vomiting response.
7. Change positions frequently give skin care with often, and keep the bed dry and free of folds.
Rational: tissue edema and circulatory disturbance tends to damage the skin.
Collaboration:
1. Monitor laboratory examinations, eg Hb / hematocrit, electrolytes, protein, albumin, BUN, creatinine.
Rationale: Provides information about hydration and organ function.
2. Give the plasma / blood, fluids, electrolytes.
Rational: Charge / maintain circulating volume and electrolyte balance. Colloid (plasma, blood) to help move the water into the area by increasing intravascular osmotic pressure.
3. Keep fasting with nasogastric aspiration / intestinal
Rational: Lowering intestinal hyperactivity, and loss from diarrhea.
Source : http://careplannursing.blogspot.com/2012/01/deficient-fluid-volume-nursing-care.html